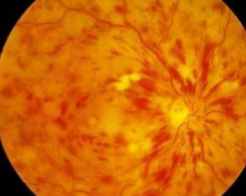
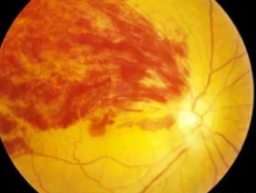
If you notice sudden blurry vision, you may have a retinal tear.
A retinal tear is an eye emergency that requires urgent medical attention.
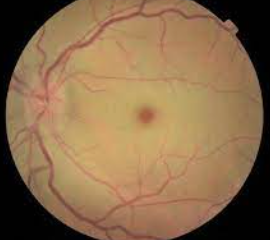
The retina is the vital layer of nerves at the back of the eye that detects light and transmits the visual signals of everything we see to the brain.
Retinal tears occur when the delicate retinal tissue gets pulled away from the back lining of the eye.
Retinal tears affect over 10% of the world’s population.
All retinal tears need to be taken seriously as they can lead to a retinal detachment, a sight-threatening eye emergency.
Symptoms of a retinal tear
A retinal tear will often produce one or more of the following symptoms:
- Flashes of light
- Blurred vision
- A sudden onset or increase of floaters
- Appearance of a shadow in your side vision
- Appearance of a gray curtain moving across your visual field
In some cases, a retinal tear may not produce any noticeable symptoms— making annual eye exams critical to your eye health.
What causes a retinal tear?
The vitreous, the gel-like substance that fills the eye, is attached to the retina at birth. As we age, the gel turns into a liquid, causing the vitreous to slowly detach from the retina.
This process, called posterior vitreous detachment (PVD), is a natural part of the aging process and rarely causes any complications.
However, a retinal tear can occur when the vitreous is ‘extra sticky’ and pulls on the retina or when it detaches too quickly.
A retinal tear can also occur following eye trauma that results in retinal bruising or scarring, making it more vulnerable to tearing.
SEE RELATED: Retinal Diseases
If you experience sudden changes to your vision, schedule an emergency consultation with an eye doctor.
Conditions that increase your risk of retinal tears
The most common risk factors for retinal tears include:
- Personal or family history of retinal tears or detachment
- Retinal degeneration
- High myopia
- Retinopathy of prematurity
- Diabetes
- Inflammatory disorders
- Certain cancers
- Autoimmune diseases
- Sickle cell disease
How are retinal tears treated?
A retinal tear is an eye emergency that requires urgent medical attention.
When treated early on, retinal tears can be effectively treated to prevent permanent vision loss from a retinal detachment.
Retinal tears are generally treated in-office using one of the following methods:
Laser surgery (photocoagulation)
This procedure uses a laser to make small burns around the retinal tear. This causes scar tissue that helps to reseal the retina to its original position on the back wall of the eye.
Freezing treatment (cryopexy)
This procedure uses a freezing probe to freeze the retinal tissue around the tear. The scar tissue that results helps to secure the retina to the back of the eye.
After treatment, follow up exams will be scheduled in order to monitor any changes in your retinal health.
LEARN MORE: Guide to Retinal Diseases
If you experience sudden changes to your vision, schedule an emergency consultation with an eye doctor.
If you notice sudden blurry vision, you may have a retinal tear.
A retinal tear is an eye emergency that requires urgent medical attention.