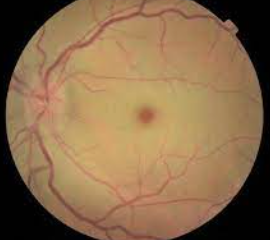
Macular edema is a leading cause of vision loss, but if detected early, can be successfully treated.
What is macular edema?
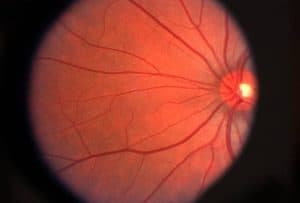
The macula is the central portion of the retina, responsible for central vision and vision for fine details.
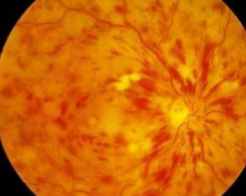
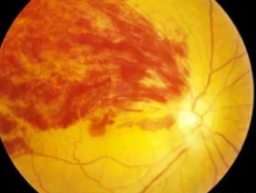
When retinal damage occurs from diabetes or other eye conditions, the macula can become swollen from a build-up of fluid.
The macula is a critical part of the eye, and good macula health is essential for clear vision. Controlling your blood sugar levels and blood pressure is the first step to protecting your eyes and preserving your vision.
Treatments for macular edema
In order to treat macular edema at its core, your eye doctor will discuss one of the following treatments:
1. Anti-VEGF injections
Macular swelling causes the VEGF protein in your body to produce blood vessels at a rapid rate. This results in the growth of abnormal blood vessels that are prone to breaking and leaking blood and fluid.
Anti-VEGF injections have revolutionized the treatment of macula edema, as many times vision can be significantly improved, even immediately after an injection.
Anti-VEGF injections help to block the VEGF proteins from producing these abnormal blood vessels, thereby reducing fluid leakage and swelling.
There are three different types of anti-VEGF medicines:
- Aflibercept (Eylea)
- Bevacizumab (Avastin)
- Ranibizumab (Lucentis)
These thin-needle injections are typically given once a month for the first six months. Then, your doctor will slowly decrease the amount of injections you receive, spreading them out over the next several years to effectively wean you off the medication.
You will notice an improvement in your vision once your blood vessels have stopped leaking.
SEE RELATED: What Is Macular Edema?
If you have noticed any new changes to your vision, contact an eye doctor near you as you may need urgent treatment for swelling in your eyes.
2. Focal-grid macular laser surgery
Focal-grid macular laser surgery helps to seal the blood vessels in the retina to stop the leaking and bring down the macular swelling.
This laser procedure is performed on one eye at a time, to give your eye a chance to heal before the other eye is treated — typically within a couple of weeks.
This procedure is generally performed in conjunction with anti-VEGF injections if the anti-VEGF medications prove to be ineffective.
3. Corticosteroids
Corticosteroids, often called steroids, target inflammation in the body and may be prescribed to reduce retinal swelling.
Steroids can be injected directly into the eye or implanted during a surgical procedure. A steroid implant offers a slow release of medicine and dissolves in the eye over time.
Steroids are generally not recommended as a first treatment as they are not as effective as the other treatments and can also lead to complications, such as cataracts and glaucoma.
4. Non-steroid eye drops
Non- steroidal anti-inflammatory medications (NSAIDs) fight inflammation without the side effects of steroids.
NSAID eye drops or oral medications may be prescribed prior to or following eye surgery in order to reduce retinal swelling.
LEARN MORE: Guide to Eye Conditions
If you experience sudden blurry vision, immediately contact an eye doctor near you.
Swelling in the macula in the back of the eye causes sudden blurry vision or vision loss.
Fortunately, if detected early, macular edema can be treated and vision can be restored.