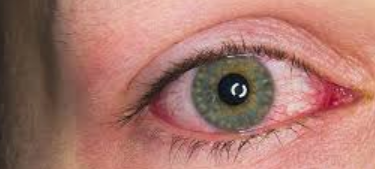
Uveitis is a sight-threatening eye disease causing 30,000 new cases of legal blindness annually in the USA and accounts for 15% of all causes of total blindness.
There are 3 types of uveitis: anterior, posterior and intermediate.
Anterior uveitis is the most common, with an incidence of over 20 per 100 000, followed by posterior/panuveitis with affects up to 4 per 100 000 person, and intermediate uveitis is the least common affecting less than 1 per 100 000 people.
What is Anterior Uveitis?
Anterior uveitis is an inflammation of the middle layer of the eye, the iris – the colored part of the eye and the adjacent organ, the ciliary body.
This condition is often referred to as ‘iritis’ as it most frequently affects the iris.
In anterior uveitis, the iris becomes inflamed and the blood vessels within the iris leak white blood cells and protein into the front part of the eye, the area behind the iris may also become inflamed.
Anterior uveitis is not an infection or contagious.
What causes anterior uveitis?
In most cases, the cause of anterior uveitis is unknown. For some patients, anterior uveitis can occur regularly. For others it can result from a trauma to the eye, such as being hit or having a foreign body in the eye.
The following conditions have also been linked to anterior uveitis:
- Rheumatoid arthritis
- Juvenile rheumatoid arthritis
- Ankylosing spondylitis
- Lupus
- Syphilis
- Gout
- Herpes virus infection
- Crohn’s disease
- Ulcerative colitis
- Psoriasis
Contact an eye doctor near you who can help treat your anterior uveitis.
SEE RELATED: Pink Eye: What Do I Do?
Symptoms of anterior uveitis
The following symptoms may occur in one or both eyes:
- Blurred vision
- Light sensitivity
- Red, sore and inflamed eye
- Small, or irregular-shaped pupil
- Throbbing eye pain
How to treat anterior uveitis
Treatment for anterior uveitis depends on what is causing it. If anterior uveitis is caused by another condition, treating that underlying condition may eliminate the inflammation.
Common treatment options for anterior uveitis include:
- Prescription eye drops which dilate the pupils, along with anti-inflammatory drugs. Dilating drops will increase light sensitivity and blur vision. However, by relaxing the iris muscles, the eye will be more comfortable.
- steroid injection medications
- Oral steroid medications
In a healthy individual, anterior uveitis generally can’t be prevented since the cause usually is not identified. However, for a person with an auto-immune disease, managing their condition can lead to improved physical health, including eye health.
Early diagnosis and proper treatment is essential to prevent serious complications, including permanent loss of some or all vision.
If untreated, cataracts, glaucoma or retinal edema can develop and cause permanent vision loss.
LEARN MORE: Guide to Eye Conditions
Schedule an eye exam with an eye doctor near you who can assess your vision and eye health.