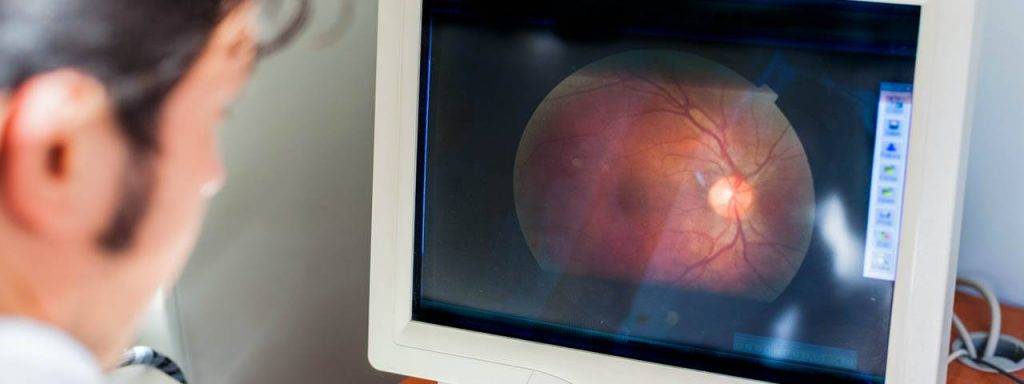
If your optometrist suspects abnormalities in the back of the eye, a fluorescein angiography may be recommended.
A fluorescein angiography (FA) is a medical examination that involves the injection of a fluorescent dye into the bloodstream.
The dye draws attention to the blood vessels in the rear of the eye, making it possible to photograph and diagnose the operation of these blood vessels. Most FAs are viewed by the doctor in black and white.
Eye doctors perform FA to confirm a diagnosis, select the best treatment option or monitor the health of the vessels in the back of your eye.
When is FA used?
Fluorescein angiography may be performed by an eye doctor to determine whether treatment for various eye disorders are effective:
- Macular degeneration
- Diabetic retinopathy
- Macular edema
- Blockage of veins inside the eye
- Macular pucker
- Ocular melanoma
FA may also be used to:
- Target treatment areas
- Track changes in an eye disease over time
SEE RELATED: The Importance of Pupil Exams
Contact an eye doctor near you to find out whether you can benefit from fluorescein angiography.
How is fluorescein angiography performed?
Fluorescein angiography is commonly performed in the office of your eye doctor. It usually takes under 30 minutes.
Here’s what to expect:
- Your eye doctor or an assistant will dilate (widen) your pupil with eye drops.
- Fluorescein, a yellowish dye, will be injected into a vein, usually in the arm. The dye takes about 10–15 seconds to pass through your body. When the dye reaches your eye’s blood vessels, it will cause them to “fluoresce,” or glow brightly.
- Your eye doctor will use a unique camera to take photographs as the dye flows across your retina. These images will help your eye doctor identify any problems and locate the vessels that need to be treated.
What to expect after fluorescein angiography
Dilating eye drops produce blurry vision and light sensitivity, which can last for several hours.
Bring sunglasses to your visit, and have someone take you home afterward because you will not be able to drive safely.
What are the risks of FA?
The most common side effects are nausea and vomiting, which are often managed at the doctor’s office.
Dry mouth or increased salivation, a faster heart rate, and sneezing are all possible side effects.
You may develop a significant allergic reaction in rare situations, which can involve the following:
- Hives
- Fainting
- Difficulty breathing
- Swelling of the larynx
- Cardiac arrest
If you’re pregnant or suspect you might be, alert your eye doctor, as the potential effect on a fetus in the womb is unknown.
LEARN MORE: Guide to Eye Exams
Contact an eye doctor near you to learn more about fluorescein angiography.